
First Rank Symptoms of Schizophrenia: Key Indicators Explained
Schizophrenia, a complex and often misunderstood mental health condition, presents a range of symptoms that can be bewildering to both patients and their loved ones. In this blog post, psychiatrist Dr. Prakhar Jain, delves into the first rank symptoms of schizophrenia, shedding light on these critical indicators that play a pivotal role in diagnosis and understanding of the condition.
Unraveling Schizophrenia’s Complexity
Navigating the Maze of Schizophrenia: A Comprehensive Understanding – Schizophrenia, a mental health disorder shrouded in complexity and often misunderstood, presents unique challenges to both those who experience it and the professionals who treat it. In this detailed guide, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricate nature of schizophrenia, focusing particularly on its first rank symptoms. This blog post is designed to shed light on the nuances of schizophrenia, offering a clearer understanding of its symptoms, impact, and the challenges it poses.
Schizophrenia is more than just a single symptom or experience; it’s a multifaceted condition that affects perception, thinking, and behavior. Understanding its symptoms is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. This article aims to demystify schizophrenia, breaking down its complexities into understandable segments, and providing a foundation for empathy and informed care for those affected by this condition.
What Are First Rank Symptoms of Schizophrenia?
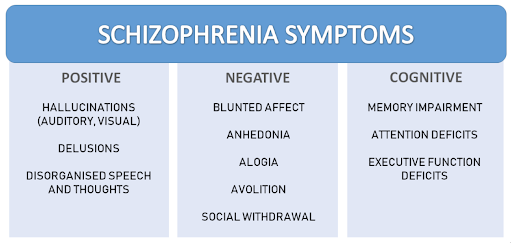
Deciphering the Core Symptoms: A Deep Dive into Schizophrenia’s Hallmarks – First rank symptoms of schizophrenia, a term coined by psychiatrist Kurt Schneider, are considered key in diagnosing this condition. This section of our guide delves into what these symptoms are and their significance in the context of schizophrenia.
Defining First Rank Symptoms: These symptoms are a group of experiences that are highly indicative of schizophrenia. They include specific types of hallucinations and delusions, thought insertion, withdrawal, and broadcasting.
Hallucinations and Delusions: Hallucinations, particularly auditory ones, are common first rank symptoms where a person might hear voices that others do not. Delusions, on the other hand, are false beliefs held with strong conviction despite evidence to the contrary.
Thought Disorders: This encompasses thought insertion (belief that thoughts are being placed in one’s mind), withdrawal (belief that thoughts are being removed), and broadcasting (belief that thoughts are being broadcasted to others).
Importance in Diagnosis: Understanding and identifying these first rank symptoms are crucial for psychiatrists in diagnosing schizophrenia, as they are strongly suggestive of the disorder.
Delusions and Hallucinations: Core Features of First Rank Symptoms
The Hallmarks of Schizophrenia: Navigating the Realms of Perception and Belief – Delusions and hallucinations stand as the most prominent and often the most distressing aspects of schizophrenia’s first rank symptoms. This section of our guide delves into these core features, exploring their nature, types, and impact on individuals with schizophrenia.
Auditory Hallucinations: Often considered the most common hallucination in schizophrenia, auditory hallucinations typically involve hearing voices or sounds that are not present. These voices can be critical, commanding, or neutral.
Visual and Other Hallucinations: While less common, visual hallucinations (seeing things that aren’t there) and other sensory hallucinations can also occur, adding to the complexity of the condition.
Nature of Delusions: Delusions in schizophrenia are firmly held beliefs that are contrary to reality. They can be paranoid (believing others are plotting against them), grandiose (having an inflated sense of self-importance), or bizarre (strange and implausible beliefs).
Impact on Behavior and Emotion: These symptoms can lead to significant distress, confusion, and fear, often impacting behavior and emotional well-being.
Understanding Thought Disorders in Schizophrenia
Decoding the Disrupted Patterns of Thought
Thought disorders are a critical component of schizophrenia’s first rank symptoms, often manifesting as disorganized thinking and communication. This part of the article focuses on understanding these thought disorders and their manifestations in schizophrenia.
Thought Insertion, Withdrawal, and Broadcasting: These specific types of thought disorders involve beliefs that one’s thoughts are being controlled, inserted, or broadcasted by external forces, leading to a profound sense of loss of privacy and autonomy.
Disorganized Thinking: This can manifest as difficulty in organizing thoughts, leading to disjointed speech and an inability to communicate effectively.
Concrete Thinking: Individuals with schizophrenia may also exhibit concrete thinking, where abstract thinking becomes difficult, and everything is interpreted in a literal sense.
Impact on Daily Functioning: Thought disorders can significantly impair daily functioning, affecting the ability to work, maintain relationships, and carry out routine tasks.
The Impact of First Rank Symptoms on Daily Life
Living with Schizophrenia: The Everyday Reality of First Rank Symptoms – The first rank symptoms of schizophrenia, while clinically significant for diagnosis, also have a profound impact on the daily lives of those affected. This section of our guide explores how these symptoms influence everyday functioning, relationships, and overall quality of life.
Challenges in Personal Relationships: Hallucinations and delusions can strain relationships, as individuals may struggle to differentiate between reality and their perceptions, leading to misunderstandings and conflicts.
Work and Education Disruptions: Thought disorders and difficulties in concentration and organization can significantly impair academic and professional performance.
Social Isolation: The stigma associated with schizophrenia, coupled with the distressing nature of the symptoms, often leads to social withdrawal and isolation.
Emotional and Psychological Strain: Constantly managing these symptoms can be emotionally exhausting, increasing the risk of co-occurring mental health issues like depression or anxiety.
Coping with Misunderstandings: Misconceptions about schizophrenia can lead to social stigma, making it challenging for individuals to seek support and understanding.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Navigating Schizophrenia’s Challenges
Deciphering Schizophrenia: From Recognition to Management – Accurately diagnosing and effectively treating schizophrenia, particularly in the context of its first rank symptoms, is crucial. This part of the article discusses the diagnostic process and the treatment options available to manage schizophrenia.
Diagnostic Process: The diagnosis of schizophrenia, particularly through the identification of first rank symptoms, involves a comprehensive psychiatric evaluation and, often, a period of observation.
Treatment Modalities: Treatment typically includes a combination of antipsychotic medications, psychotherapy, and support services. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and type of symptoms, as well as individual patient needs.
Role of Psychotherapy: Therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can be effective in helping individuals manage delusions and hallucinations, and in improving thought processes.
Support Systems: Family therapy and community support play a crucial role in the treatment process, providing the necessary support and understanding.
Ongoing Management: Managing schizophrenia is a long-term process, often requiring ongoing treatment and adjustment of strategies to handle symptoms effectively.
Conclusion: Empathy and Understanding in Mental Health
Fostering Compassion in the Face of Schizophrenia – As we conclude our exploration of the first rank symptoms of schizophrenia, it’s important to recognize the critical role of empathy and understanding in mental health care. This final section reflects on the importance of compassion in dealing with schizophrenia, both for those experiencing it and for their support networks.
Breaking Down Stigma: Educating society about schizophrenia and dispelling myths is essential in reducing stigma and fostering a more compassionate environment.
Empowering Individuals: Empowering those with schizophrenia through education, support, and effective treatment options is key to improving their quality of life.
The Value of Support: The support of family, friends, and mental health professionals is invaluable in the journey of managing schizophrenia.
A Call for Greater Understanding: This guide serves as a call to deepen our understanding of schizophrenia, to approach it with empathy, and to provide the necessary support to those affected.
